Page 40
Arthroplasty 2019
June 24-25, 2019
Volume 14
Journal of Orthopaedics Trauma Surgery and Related Research
Arthroplasty
June 24-25, 2019 | Rome, Italy
12
th
International Conference on
Premature fracture of a modular femoral neck after total hip arthroplasty: Comparison of two different
stem-neck alloys
Monika Jenko
Institute of Metals and Technology, Slovenia
Statement of the Problem:
An alarmingly large number of femoral modular stems of titanium alloy neck suffer from
premature fractures. The cobalt-chromium neck was introduced for its better wear and mechanical properties, although it
fails even earlier. Until now there were no direct comparisons between two different femoral modular necks for the same
type of stem implant. Experts from orthopaedic surgery and metallurgy have combined their research efforts to compare
the femoral modular stem-necks of similar titanium and dissimilar titanium/cobalt-chromium alloy systems from the
clinical and metallurgical points of view.
Orientation:
Two premature fractured modular neck Hip endoprostheses of similar and dissimilar metals systems were
investigated. Multivariate analyses were performed to assess the differences in the fretting, corrosion and fatigue of
similar alloys and dissimilar alloys modular joints. Patient’s demographic information was collected frommedical records.
Findings:
Similar stem-neck metals of hip endoprostheses failed due to continuous dynamic micro-motions, crevice
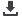
corrosion, fretting and fatigue, as well as improper neck dimensions. Themechanismof titaniumalloymodular neck fracture
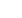
is shown inFigure 1.The dissimilarmetals stem-neck fractureddue to continuous dynamicmicro-motions, selective leaching
of cobalt ions from the cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy and formation of titan-chromium-molybdenum interfacial
phase and severe crevice corrosion. The mechanism of cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy modular neck fracture is
shown in Figure 2 The dissimilar joints suffered more corrosion than the similar joints due to additional galvanic corrosion.
Conclusions:
Fretting, corrosion and fatigue occurred on both neck-stem retrievals of the similar and dissimilar metals. Both
metal-alloysystemsusedinthisapplicationareknowntobehighlycorrosionresistantandgivingrisetothebio-tribo-corrosion
processes needs to be understood and characterized so that appropriate changes in design and materials can be upgrade.
J.Orthop.Trauma Surg.Relat.Res. | Volume 14
ISSN:2449-9145